Difference between revisions of "ESP8266 Serial WIFI Module"
(Created page with "==Overview== rightESP8266 offers a complete and self-contained Wi-Fi networking solution, allowing it to either host the application or...") |
(No difference)
|
Revision as of 09:18, 16 September 2014
Contents
Overview
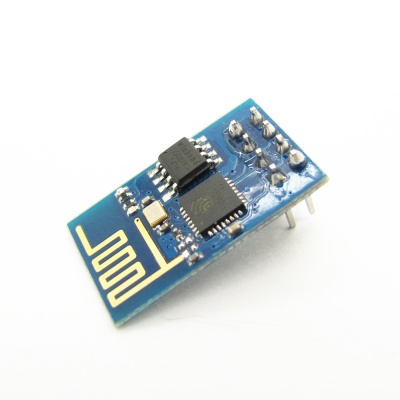
ESP8266 offers a complete and self-contained Wi-Fi networking solution, allowing it to either host the application or to offload all Wi-Fi networking functions from another application processor.When ESP8266 hosts the application, and when it is the only application processor in the device, it is able to boot up directly from an external flash. It has integrated cache to improve the performance of the system in such applications, and to minimize the memory requirements.
Alternately, serving as a Wi-Fi adapter, wireless internet access can be added to any microcontroller-based design with simple connectivity through UART interface or the CPU AHB bridge interface.
ESP8266 on-board processing and storage capabilities allow it to be integrated with the sensors and other application specific devices through its GPIOs with minimal development up-front and minimal loading during runtime. With its high degree of on-chip integration, which includes the antenna switch balun, power management converters, it requires minimal external circuitry, and the entire solution, including front-end module, is designed to occupy minimal PCB area.
Sophisticated system-level features include fast sleep/wake context switching for energy-efficient VoIP, adaptive radio biasing for low-power operation, advance signal processing, and spur cancellation and radio co-existence features for common cellular, Bluetooth, DDR, LVDS, LCD interference mitigation.
Go shopping [ESP8266 Serial WIFI Module(IM140905002)]
Electronic Characteristics
1.Current Consumption
The following current consumption is based on 3.3V supply, and 25℃ ambient, using internal regulators. Measurements are done at antenna port without SAW filter. All the transmitter’s measurements are based on 90% duty cycle, continuous transmit mode.
| Mode | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
| Transmit 802.11b, CCK 1Mbps, POUT=+19.5dBm | 215 | mA | ||
| Transmit 802.11b, CCK 11Mbps, POUT=+18.5dBm | 197 | mA | ||
| Transmit 802.11g, OFDM 54Mbps, POUT =+16dBm | 145 | mA | ||
| Transmit 802.11n, MCS7, POUT=+14dBm | 135 | mA | ||
| Receive 802.11b, packet length=1024 byte, -80dBm | 60 | mA | ||
| Receive 802.11g, packet length=1024 byte, -70dBm | 60 | mA | ||
| Receive 802.11n, packet length=1024 byte, -65dBm | 62 | mA | ||
| Standby | 0.9 | mA | ||
| Deep sleep | 10 | uA | ||
| Power save mode DTIM 1 | 1.2 | mA | ||
| Power save mode DTIM 3 | 0.86 | mA | ||
| Total shutdown | 0.5 | uA |
2.RF Performance
The following are measured under room temperature conditions with 3.3V and 1.1V power supplies.
| Description | Min | Typical | Max | Unit |
| Input frequency | 2412 | 2484 | MHz | |
| Input impedance | 50 | Ω | ||
| Input reflection | -10 | dB | ||
| Output power of PA for 72.2Mbps | 14 | 15 | 16 | dBm |
| Output power of PA for 11b mode | 17.5 | 18.5 | 19.5 | dBm |
| Sensitivity | ||||
| CCK, 1Mbps | -98 | dBm | ||
| CCK, 11Mbps | -91 | dBm | ||
| 6Mbps (1/2 BPSK) | -93 | dBm | ||
| 54Mbps (3/4 64-QAM) | -75 | dBm | ||
| HT20, MCS7 (65Mbps, 72.2Mbps) | -71 | dBm |
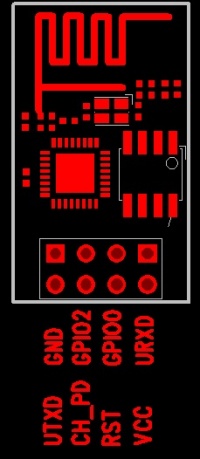
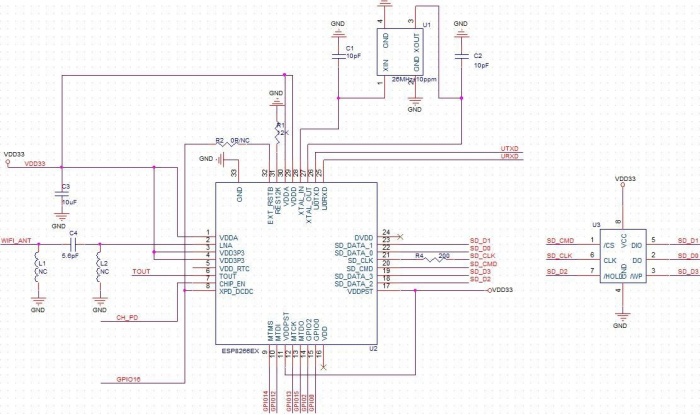
Hardware
Schematic
Application Notes
- Smart power plugs
- Home automation
- Mesh network
- Industrial wireless control
- Baby monitors
- IP Cameras
- Sensor networks
- Wearable electronics
- Wi-Fi location-aware devices
- Security ID tags
- Wi-Fi position system beacons
Firmware & Software Development Kit
The application and firmware is executed in on-chip ROM and SRAM, which loads the instructions during wake-up, through the SDIO interface, from the external flash. The firmware implements TCP/IP, the full 802.11 b/g/n/e/i WLAN MAC protocol and Wi-Fi Direct specification. It supports not only basic service set (BSS) operations under the distributed control function (DCF) but also P2P group operation compliant with the latest Wi-Fi P2P protocol. Low level protocol functions are handled automatically by ESP8266:
- RTS/CTS
- acknowledgement
- fragmentation and defragmentation
- aggregation
- frame encapsulation (802.11h/RFC 1042)
- utomatic beacon monitoring / scanning
- P2P Wi-Fi direct
Passive or active scanning, as well as P2P discovery procedure is performed autonomously once initiated by the appropriate command. Power management is handled with minimum host interaction to minimize active duty period.
Features:
- 802.11 b/g/n/d/e/i/k/r support;
- Wi-Fi Direct (P2P) support:
- P2P Discovery, P2P Group Owner mode, P2P Power Management
- Infrastructure BSS Station mode / P2P mode / softAP mode support;
- Hardware accelerators for CCMP (CBC-MAC, counter mode), TKIP (MIC, RC4), WAPI (SMS4), WEP (RC4), CRC;
- WPA/WPA2 PSK, and WPS driver;
- Additional 802.11i security features such as pre-authentication, and TSN;
- Open Interface for various upper layer authentication schemes over EAP such as TLS, PEAP, LEAP, SIM, AKA, or customer specific;
- 802.11n support (2.4GHz / 5GHz);
- Supports MIMO 11 and 21, STBC, A-MPDU and A-MSDU aggregation and 0.4s guard interval;
- WMM power save U-APSD;
- Multiple queue management to fully utilize traffic prioritization defined by 802.11e standard;
- UMA compliant and certified;
- 802.1h/RFC1042 frame encapsulation;
- Scattered DMA for optimal CPU off load on Zero Copy data transfer operations;
- Antenna diversity and selection (software managed hardware);
- Clock/power gating combined with 802.11-compliant power management dynamically adapted to curent connection condition providing minimal power consumption;
- Adaptive rate fallback algorithm sets the optimium transmission rate and Tx power based on actual SNR and packet loss information;
- Automatic retransmission and response on MAC to avoid packet discarding on slow host environment;
- Seamless roaming support;
- Configurable packet traffic arbitration (PTA) with dedicated slave processor based design provides flexible and exact timing Bluetooth co-existence supoport for a wide range of Bluetooth Chip vendors;
- Dual and single antenna Bluetooth co-existence support with optional simultaneous receive (Wi-Fi/Bluetooth) capability.
AT Commands
Format
- Baud rate at 57600
- x is the commands
| Set | Inquiry | Test | Execute |
|---|---|---|---|
| AT+<x>=<…> | AT+<x>? | AT+<x>=? | AT+<x> |
| AT+CWMODE=<mode> | AT+CWMODE? | AT+CWMODE=? | - |
| Set the network mode | Check current mode | Return which modes supported | - |
Commands
- carefully there are must be no any spaces between the " and IP address or port
|
Commands |
Description |
Type |
Set/Execute |
Inquiry |
test |
Parameters and Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
AT |
general test |
basic |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
AT+RST |
restart the module |
basic |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
AT+GMR |
check firmware version |
basic |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
AT+CWMODE |
wifi mode |
wifi |
AT+CWMODE=<mode> |
AT+CWMODE? |
AT+CWMODE=? |
1= Sta, 2= AP, 3=both, Sta is the default mode of router, AP is a normal mode for devices |
|
AT+CWJAP |
join the AP |
wifi |
AT+ CWJAP =<ssid>,< pwd > |
AT+ CWJAP? |
- |
ssid = ssid, pwd = wifi password |
|
AT+CWLAP |
list the AP |
wifi |
AT+CWLAP |
|||
|
AT+CWQAP |
quit the AP |
wifi |
AT+CWQAP |
- |
AT+CWQAP=? |
|
|
AT+ CWSAP |
set the parameters of AP |
wifi |
AT+ CWSAP= <ssid>,<pwd>,<chl>, <ecn> |
AT+ CWSAP? |
ssid, pwd, chl = channel, ecn = encryption; eg. Connect to your router: AT+CWJAP="www.electrodragon.com","helloworld"; and check if connected: AT+CWJAP? |
|
|
AT+CWLIF |
check join devices' IP |
wifi |
AT+CWLIF |
- |
- |
|
|
AT+ CIPSTATUS |
get the connection status |
TCP/IP |
AT+ CIPSTATUS |
<id>,<type>,<addr>,<port>,<tetype>= client or server mode |
||
|
AT+CIPSTART |
set up TCP or UDP connection |
TCP/IP |
1)single connection (+CIPMUX=0) AT+CIPSTART= <type>,<addr>,<port>; 2) multiple connection (+CIPMUX=1) AT+CIPSTART= <id><type>,<addr>, <port> |
- |
AT+CIPSTART=? |
id = 0-4, type = TCP/UDP, addr = IP address, port= port; eg. Connect to another TCP server, set multiple connection first: AT+CIPMUX=1; connect: AT+CIPSTART=4,"TCP","X1.X2.X3.X4",9999 |
|
AT+CIPMODE |
set data transmission mode |
TCP/IP |
AT+CIPMODE=<mode> |
AT+CIPSEND? |
0 not data mode, 1 data mode; return "Link is builded" |
|
|
AT+CIPSEND |
send data |
TCP/IP |
1)single connection(+CIPMUX=0) AT+CIPSEND=<length>; 2) multiple connection (+CIPMUX=1) AT+CIPSEND= <id>,<length> |
AT+CIPSEND=? |
eg. send data: AT+CIPSEND=4,15 and then enter the data. |
|
|
AT+CIPCLOSE |
close TCP or UDP connection |
TCP/IP |
AT+CIPCLOSE=<id> or AT+CIPCLOSE |
AT+CIPCLOSE=? |
||
|
AT+CIFSR |
Get IP address |
TCP/IP |
AT+CIFSR |
AT+ CIFSR=? |
||
|
AT+ CIPMUX |
set mutiple connection |
TCP/IP |
AT+ CIPMUX=<mode> |
AT+ CIPMUX? |
0 for single connection 1 for multiple connection |
|
|
AT+ CIPSERVER |
set as server |
TCP/IP |
AT+ CIPSERVER= <mode>[,<port> ] |
mode 0 to close server mode, mode 1 to open; port = port; eg. turn on as a TCP server: AT+CIPSERVER=1,8888, check the self server IP address: AT+CIFSR=? |
||
|
AT+ CIPSTO |
Set the server timeout |
AT+CIPSTO=<time> |
AT+CIPSTO? |
<time>0~28800 in second |
||
|
+IPD |
received data |
For Single Connection mode(CIPMUX=0): + IPD, <len>: |
Download
File:ESP8266_Specifications_English.pdf File:ESP8266 Specifications(Chinese).pdf
Useful Link
Reference:
 Notice
Notice