Difference between revisions of "PSF-A85"
m (→Hardware) |
m (→Pin Definitions) |
||
| Line 128: | Line 128: | ||
==Pin Definitions== | ==Pin Definitions== | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[File:ITEAD8285_pinmap.jpg|500px]] |
| − | { class=wikitable | + | {| class="wikitable" |
| − | ! scope=col | + | ! scope="col" | PIN || scope="col" | Function || scope="col" | Description |
| − | - | + | |- |
| − | + | | style="text-align:right" | 1 || ANT || WiFi Antenna | |
| − | - | + | |- |
| − | + | | style="text-align:right" | 2 || ADC || ADC, input range: 0V-1V; | |
| − | - | + | |- |
| − | + | | style="text-align:right" | 3 || EN || Chip enable terminal. Active high: chip works normally; | |
| − | Active low chip close, very small current. | + | Active low: chip close, very small current. |
| − | - | + | |- |
| − | + | | style="text-align:right" | 4 || GPIO16 || GPIO16 | |
| − | - | + | |- |
| − | + | | style="text-align:right" | 5 || GPIO14 || GPIO14; HSPI_CLK | |
| − | - | + | |- |
| − | + | | style="text-align:right" | 6 || GPIO12 || GPIO12; HSPI_MISO | |
| − | - | + | |- |
| − | + | | style="text-align:right" | 7 || GPIO13 || GPIO13; HSPI_MOSI; UART0_CTS | |
| − | - | + | |- |
| − | + | | style="text-align:right" | 8 || GPIO15 || GPIO15; HSPI_CS; UART0_RTS | |
| − | - | + | |- |
| − | + | | style="text-align:right" | 9 || GPIO2 || Also used as a programming flash UART1_TX;GPIO2 | |
| − | - | + | |- |
| − | + | | style="text-align:right" | 10 || GPIO0 || GPIO0; SPI_CS2 | |
| − | - | + | |- |
| − | + | | style="text-align:right" | 11 || GPIO4 || GPIO4 | |
| − | - | + | |- |
| − | + | | style="text-align:right" | 12 || GND || GND | |
| − | - | + | |- |
| − | + | | style="text-align:right" | 13 || GPIO9 || PIHD;HSPIHD;GPIO9 | |
| − | - | + | |- |
| − | + | | style="text-align:right" | 14 || GPIO10 || SPIWP;HSPIWP;GPIO10 | |
| − | - | + | |- |
| − | + | | style="text-align:right" | 15 || GPIO11 || SPI_CS0;GPIO11 | |
| − | - | + | |- |
| − | + | | style="text-align:right" | 16 || GPIO6 || SPI_CLK;GPIO6 | |
| − | - | + | |- |
| − | + | | style="text-align:right" | 17 || GPIO7 || SPI_MSIO;GPIO7 | |
| − | - | + | |- |
| − | + | | style="text-align:right" | 18 || GPIO8 || SPI_MOSI;GPIO8 | |
| − | - | + | |- |
| − | + | | style="text-align:right" | 19 || GPIO5 || GPIO5 | |
| − | - | + | |- |
| − | + | | style="text-align:right" | 20 || GND || GND | |
| − | - | + | |- |
| − | + | | style="text-align:right" | 21 || RX || Also used as a programming flash UART Rx;GPIO3 | |
| − | - | + | |- |
| − | + | | style="text-align:right" | 22 || TX || Also used as a programming flash UART Tx ;GPIO1;SPI_CS1 | |
| − | - | + | |- |
| − | + | | style="text-align:right" | 23 || 3V3 || Power supply | |
| − | - | + | |- |
| − | + | | style="text-align:right" | 24 || RESET || External reset(low active) | |
| − | } | + | |} |
==Power Consumption== | ==Power Consumption== | ||
Revision as of 07:22, 8 July 2016
Contents
Overview
The PSF-A85 is an ultra low-power Wi-Fi module designed by ITEAD. The module adopts the highly integrated Wi-Fi chip ESP8285. It features industry's highly competitive packaging size and ultra-low power technology. Specially designed for mobile devices and the Internet of Things application, it connects physical devices to Wi-Fi wireless network to make Internet or LAN communications.
PSF-A85 has completed self-contained wireless network, with built-in 32-bit kernel processor, on-chip SRAM, it can be used as the main control chip, but also as a WiFi adapter. To apply it to other microcontroller based designs, simply by using SPISDIO or I2CUART interface to communicate.
The module supports IPEX connector and stamp hole interface. It can be widely apply for smart power grid, smart transportation, smart home, handheld devices, industrial control, etc.
Go shopping PSF-A85 WiFi Wireless Module
Features
802.11 bgndeikr
Support STAAPSTA+AP mode
WPAWPA2 PSK and WP
Built-in TCPIP protocol stack, support multi-way TCP Client connection
Support rich Socket AT commands
Support UARTGPIO data communication interface
Built-in 32 bit MCU, also work as application processor
3.3V single supply
Wi-Fi Direct (P2P) support
Support MIMO 1×1 and 2×1, STBC, A- MPDU and A-MSDU aggregation and 0.4μs guard interval
WMM power save U-APSD
Multiple queue management to fully utilize traffic prioritization defined by 802.11e standard.
Adaptive rate fallback algorithm sets the optimum transmission rate and Tx power based on actual SNR and packet loss information.
Functions
Main functions
The main function of PSF-A85 includes serial transparent transmission, PWM control, GPIO control.
Serial transparent transmission good transmission performance, the maximum transmission rate is 460800bps.
PWM control adjust lighting, adjust led color, adjust motor speed and much more.
GPIO control control switches, relay and more.
Operating Mode
STA mode the module connected to Internet via a router, thus mobile phone or computer can remote control devices via Internet.
AP mode PSF-A85 module worked as a hotspot, which realizes directly communication between the module and phonecomputer, enables wireless LAN control.
STA+AP mode this is coexistence mode, which can realize seamlessly switch via the Internet control, easy to operate.
Applications
Serial to Wi-Fi; Industrial transparent transmission DTU; Wi-Fi remote monitoringcontrol; Intelligent Toy; Color LED control; Firefighting and security integrated intelligence management; Intelligent card terminals, wireless POS machines, Wi-Fi cameras, hand-held devices, etc.
Main Technical Specifications
| Module | Type | PSF-A85 |
|---|---|---|
| Chip | ESP8285 | |
| Wi-Fi | Wireless Standard | IEEE 802.11b/g/n/d/e/i/k/r |
| Frequency Range | 2.412GHz-2.484GHz | |
| Tx Power | 802.11b: +20 +/-2dBm (@11Mbps) | |
| 802.11g: +17 +/-2dBm (@54Mbps) | ||
| 802.11n: +14 +/-2dBm (@HT20, MCS7) | ||
| Rx Sensitivity | 802.11b: -91 dBm (@11Mbps ,CCK) | |
| 802.11g: -75 dBm (@54Mbps, OFDM) | ||
| 802.11n: -72 dBm (MCS7) | ||
| Connector | External:stamp hole interface | |
| External:I-PEX connector | ||
| Hardware | Peripheral Interface | UART,IIC,PWM,GPIO,ADC |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V | |
| GPIO Drive capability | Max:12mA | |
| Operating Current | Continue sending=>Average value:~70mA, Peak value: 200mA
Normal mode=> Average value: ~12mA, Peak value: 200mA Standby:<200uA | |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40℃~125℃ | |
| Storage Temperature Range | Temp.:<40℃, Relative humidity:<90%R.H. | |
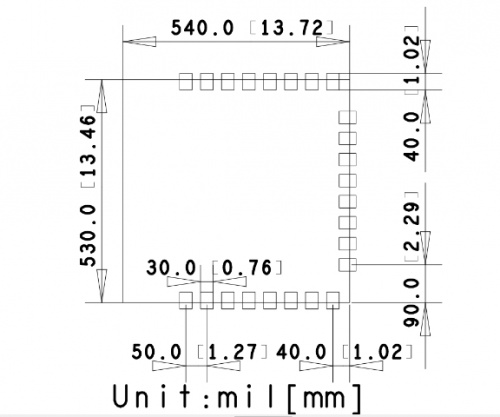
| Size | 13.5mm*13.7mm*1mm; | |
| Serial transparent transmission | Transmission rate | 110-921600bps |
| TCP Client | 5 | |
| Software | Wireless network types | STA/AP/STA+AP |
| Security | WEP/WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK | |
| Encryption | WEP64/WEP128/TKIP/AES | |
| Firmware Upgrade | UART Download / OTA (via network) | |
| Network Protocols | IPv4, TCP/UDP/FTP/HTTP |
Hardware
PSF-A85 has many interfaces, supports UART, IIC, PWM, GPIO, ADC, etc., suitable for a variety of networking applications.
We can offer PSF-A85 module PCB package, please contact customer service if you need;
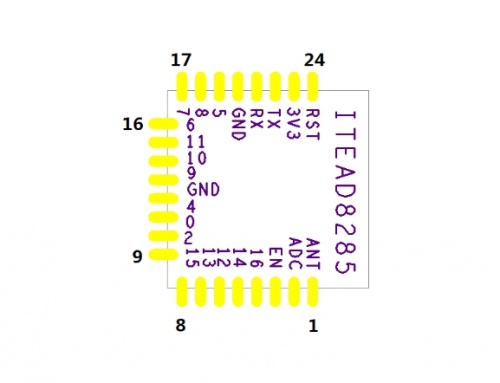
Pin Definitions
| PIN | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ANT | WiFi Antenna |
| 2 | ADC | ADC, input range: 0V-1V; |
| 3 | EN | Chip enable terminal. Active high: chip works normally;
Active low: chip close, very small current. |
| 4 | GPIO16 | GPIO16 |
| 5 | GPIO14 | GPIO14; HSPI_CLK |
| 6 | GPIO12 | GPIO12; HSPI_MISO |
| 7 | GPIO13 | GPIO13; HSPI_MOSI; UART0_CTS |
| 8 | GPIO15 | GPIO15; HSPI_CS; UART0_RTS |
| 9 | GPIO2 | Also used as a programming flash UART1_TX;GPIO2 |
| 10 | GPIO0 | GPIO0; SPI_CS2 |
| 11 | GPIO4 | GPIO4 |
| 12 | GND | GND |
| 13 | GPIO9 | PIHD;HSPIHD;GPIO9 |
| 14 | GPIO10 | SPIWP;HSPIWP;GPIO10 |
| 15 | GPIO11 | SPI_CS0;GPIO11 |
| 16 | GPIO6 | SPI_CLK;GPIO6 |
| 17 | GPIO7 | SPI_MSIO;GPIO7 |
| 18 | GPIO8 | SPI_MOSI;GPIO8 |
| 19 | GPIO5 | GPIO5 |
| 20 | GND | GND |
| 21 | RX | Also used as a programming flash UART Rx;GPIO3 |
| 22 | TX | Also used as a programming flash UART Tx ;GPIO1;SPI_CS1 |
| 23 | 3V3 | Power supply |
| 24 | RESET | External reset(low active) |
Power Consumption
The following data are conducted at 25°temperature with 3.3V power supply.
1. All measurements were performed at the antenna interface.
2. All transmitted data are conducted based on a 90% duty cycle, continuous transmission mode.
{ class=wikitable ! scope=col Mode scope=col Typical scope=col Unit -
Transmit 802.11b,CCK 1Mbps,Pout=+19.5dBm style=text-alignright 215 mA
-
Transmit 802.11b,CCK 11Mbps,Pout=+18.5dBm style=text-alignright 197 mA
-
Transmit 802.11g,OFDM54 Mbps,Pout=+16dBm style=text-alignright 145 mA
-
Transmi t802.11n,MCS7,Pout=+14dBm style=text-alignright 135 mA
-
Transmit 802.11b, 1024-byte packet length, -80dBm style=text-alignright 100 mA
-
Transmit 802.11g, 1024-byte packet length, -70dBm style=text-alignright 100 mA
-
Transmit 802.11n, 1024-byte packet length, -65dBm style=text-alignright 102 mA
-
System Standby mode style=text-alignright 70 mA
-
Power off style=text-alignright 0.5 μA
}
Wi-Fi Radio Characteristics
The following data are from tests conducted at room temperature with 3.3V power supply.
Note:
1. 72.2Mbps is measured under 802.11n mode, MCS = 7, GI = 200uS;
2. Maximum output power can be + 19.5dBm in 802.11b mode;
{ class=wikitable ! scope=col Parameters scope=col Min scope=col Typical scope=col Max scope=col Unit -
Input frequency 2412 - 2484 MHz
-
Input impedance - 50 Ω
-
Input reflection - - -10 dB
-
Output power of PA for 72.2 Mbp 14 15 16 dBm
-
Output power of PA for 802.11b 17.5 18.5 19.5 dBm
-
colspan=5 Sensitivity
-
CCK 1Mbps - -98 - dBm
-
CCK 11Mbps - -91 - dBm
-
6Mbps(12BPSK) - -93 - dBm
-
54Mbps(34 64-QAM) - -75 - dBm
-
HT20,MCS7(65Mbps,72.2Mbps) - -71 - dBm
-
colspan=5 Adjacent Channel Rejection
-
OFDM,6Mbps - 37 - dB
-
OFDM,54Mbps - 21 - dB
-
HT20,MCS0 - 37 - dB
-
HT20,MCS7 - 20 - dB
}
WiFi Antenna
PSF-A85 supports two kinds of antenna interfaceIPEX interfaces and stamp hole interface. You can directly use on-board PCB antenna and IPEX antenna, without adding any matching circuit. If you need to design antenna on a large board, you can use PSF-A85 stamp hole antenna interface.
Recommended Temperature Graph
Refer to IPCJEDEC standard; Peak Temperature 250°C; Number of Times ≤2 times;
FilePSF-A85_Recommended_reflux_graph.jpg550px
Related Terminologies
{ class=wikitable ! scope=col Abbreviation scope=col Description -
WiFi Wireless Fidelity
-
UART Universal Asynchronous Receiver & Transmitter
-
DTIM Delivery Traffic Indication Message
-
SOC System On a Chip
-
P2P Point to Point
-
TCP Transmission Control Protocol
-
IP Internet Protocol
-
STBC Space-Time Block Coding
-
MIMO Multiple Input Multiple Output
-
MPDU MAC Protocol Data Unit
-
MSDU MAC Server Data Unit
-
IEEE Institute Of Electrical And Electronics Engineers
-
bps Bits Per Second
-
CCK Corporate Control Key
-
DQPSK Differential Quadrature Phase Shift Keying
-
DBPSK Differential Binary Phase Shift Keying
-
QAM Quadrature Amplitude Modulation
-
OFDM Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing
-
WPA Wi-Fi Protected Access
-
WPS Wi-Fi Protected Setup
-
TKIP Temporal Key Integrity Protocol
-
WAPI Wlan Authentication And Privacy Infrastructure
-
WEP Wired Equivalent Privacy
-
CRC Cyclic Redundancy Check
}
 Notice
Notice